The Certified Application Security Engineer (CASE JAVA) credential is developed in partnership with large application and software development experts globally.
The CASE credential tests the critical security skills and knowledge required throughout a typical software development life cycle (SDLC), focusing on the importance of the implementation of secure methodologies and practices in today’s insecure operating environment.
The CASE certified training program is developed concurrently to prepare software professionals with the necessary capabilities that are expected by employers and academia globally.It is designed to be a hands-on, comprehensive application security course that will help software professionals create secure applications.
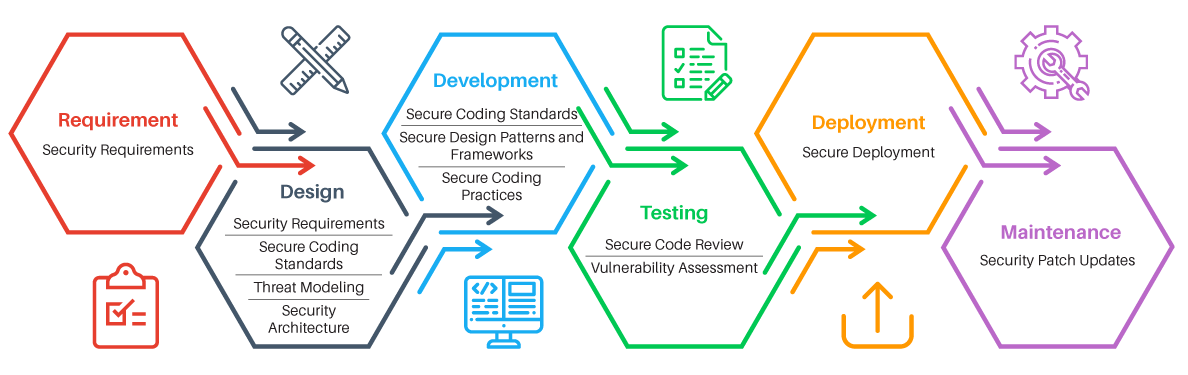
The training program encompasses security activities involved in all phases of the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC): planning, creating, testing, and deploying an application.
Unlike other application security trainings, CASE goes beyond just the guidelines on secure coding practices and includes secure requirement gathering, robust application design, and handling security issues in post development phases of application development.
This makes CASE one of the most comprehensive certifications on the market today. It is desired by software application engineers, analysts, testers globally, and respected by hiring authorities.
According to the 2017 State of Software Security Report, nearly 90% of Java applications contain one or more vulnerable component/s, making them ideal breach points for hostile attackers.
Although Java has come a long way from its development in 1995, cyber crime has also spread, reaching epidemic levels, increasing the need for secure Java developers, regardless of whether they’re creating a new program or upgrading revising an old one
The Purpose of CASE Is
- To ensure that application security is no longer an afterthought but a foremost one.
- To lay the foundation required by all application developers and development organizations, to produce secure applications with greater stability and fewer security risks to the consumer, therefore, making security a foremost thought.
- To ensure that the organizations mitigate the risk of losing millions due to security compromises that may arise with every step of application development process.
- To help individuals develop the habit of giving importance to security sacrosanct of their job role in the SDLC, therefore opening security as the main domain for testers, developers, network administrator etc.
Secure Software Development Process
The Certified Application Security Engineer (CASE) training and certification program provides a comprehensive application security approach which encompasses security activities involved in all the phases of Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC).
What You Will Learn
- In-depth understanding of secure SDLC and secure SDLC models
- Knowledge of OWASP Top 10, threat modelling, SAST and DAST
- Capturing security requirements of an application in development
- Defining, maintaining, and enforcing application security best practices
- Performing manual and automated code review of application
- Conducting application security testing for web applications to assess the vulnerabilities
- Driving development of a holistic application security program
- Rating the severity of defects and publishing comprehensive reports detailing associated risks and mitigations
- Working in teams to improve security posture
- Application security scanning technologies such as AppScan, Fortify, WebInspect, static application security testing (SAST), dynamic application security testing (DAST), single sign-on, and encryption
- Following secure coding standards that are based on industry-accepted best practices such as OWASP Guide, or CERT Secure Coding to address common coding vulnerabilities.
- Creating a software source code review process that is a part of the development cycles (SDLC, Agile, CI/CD)
Why Become a Certified Application Security Engineer
Immediate Credibility: The CASE program affirms that you are indeed an expert in application security. It also demonstrates the skills that you possess for employers globally.
Pertinent Knowledge: Through the CASE certification and training program, you will be able to expand your application security knowledge.
Multifaceted Skills: CASE can be applied to a wide variety of platforms, such as, mobile applications, web applications, IoT devices, and many more.
A Holistic Outlook: Ranging from pre-deployment to post-deployment security techniques, covering every aspect of secure – software development life cycle, CASE arms you with the necessary skills to build a secure application.
Better Protect and Defend: By making an application more secure you are also helping defend both organizations and individuals globally. As a CASE, it is in your hands to protect and defend and ultimately help build a safer world.
Duration: 24 hours or 3 full-day sessions
Course Material:
All attendees will receive their personal copy of the CASE courseware, an EC-Council CASE exam voucher, and access to iLabs (EC-Council’s cloud driven labs environment)
Certification:
The CASE exam can be challenged after attending the official CASE training. Candidates that successfully pass the exam will receive their CASE certificate and membership privileges. Members are expected to adhere to the policies of EC-Council’s Continuing Education Requirements.
Course Outline
- Understanding Application Security, Threats, and Attacks
- Security Requirements Gathering
- Secure Application Design and Architecture
- Secure Coding Practices for Input Validation
- Secure Coding Practices for Authentication and Authorization
- Secure Coding Practices for Cryptography
- Secure Coding Practices for Session Management
- Secure Coding Practices for Error Handling
- Static and Dynamic Application Security Testing (SAST & DAST)
- Secure Deployment and Maintenance
Course Features
- Lecture 0
- Quiz 0
- Duration 3 days
- Skill level All levels
- Language English
- Students 0
- Assessments Yes






